Automotive projects carried out in the CAMT CENTER
2021
Acronym: BioniAMoto
Coordinator: Wroclaw University of Science and Technology
Partners: Poznań University of Technology; EDAG Engineering Poland Sp z o.o.
Duration: 2021 – 2024
Funding: NCBR, TECHMATSTRATEG-III/0044/2019
Objective: Application of Additive Manufacturing (AM) technologies creates new opportunities of manufacturing complex geometries without increasing costs of manufacturing. Additional benefits of using AMtechnologies could be achieved thanks to implementation of topology optimization tools during the design process. During the BioniAMoto project, new tools for manufacturing of structural nodes for the automotive industry will be developed and prepared for implementation, such as bionic topology optimization and AM based manufacturing process from aluminium alloys. As a result of the project anew concept for manufacturing 3Dimensional nodes for structural frame of vehicles will be developed. The geometry of structural nodes will be topology optimised in order to transfer loads, using innovative generative algorithms, and joined together with available and commonly used extruded aluminium profiles.
The aim of the BioniAMoto is to achieve comparable mechanical properties for aluminium alloys processed in AM, compared to conventional type of material, mass reduction of manufactured structural nodes, remaining its stiffness and toughness at least on the same or higher level. Additionally, during the project different ways to join AM part with extruded profiles will be evaluated,without implementing extra thermal stress (eg. shaped joint, bonding, or clinching).

2019
Acronym: AM-Crash
Coordinator: Technische Universität Chemnitz (since 2021 r.)
Partners: EDAG Engineering GmbH; Salzgitter Mannesmann Forschung GmbH; Simufact Engineering GmbH; Wadim Plast Sp. z o. o.; Technische Universität Chemnitz (coordinator since 2021), EDAG (coordinator up to 2021); Wroclaw University of Science and Technology.
Duration: 2019 – 2021
Funding: NCBR – M-ERA.NET Call 2018
Objective: The aim of AM-Crash is to achieve equivalent mechanical properties of LAM components compared to standard deep-drawn parts. This will create significant cost and lead-time benefits using LAM parts for prototype vehicles during car development for crash tests, for small batch series components and for spare parts. The identical structural behavior of LAM components and deep-drawn sheet metal will be achieved by a multifactorial approach combining a specific LAM processing with suitable post treatment and joining/integration technologies.
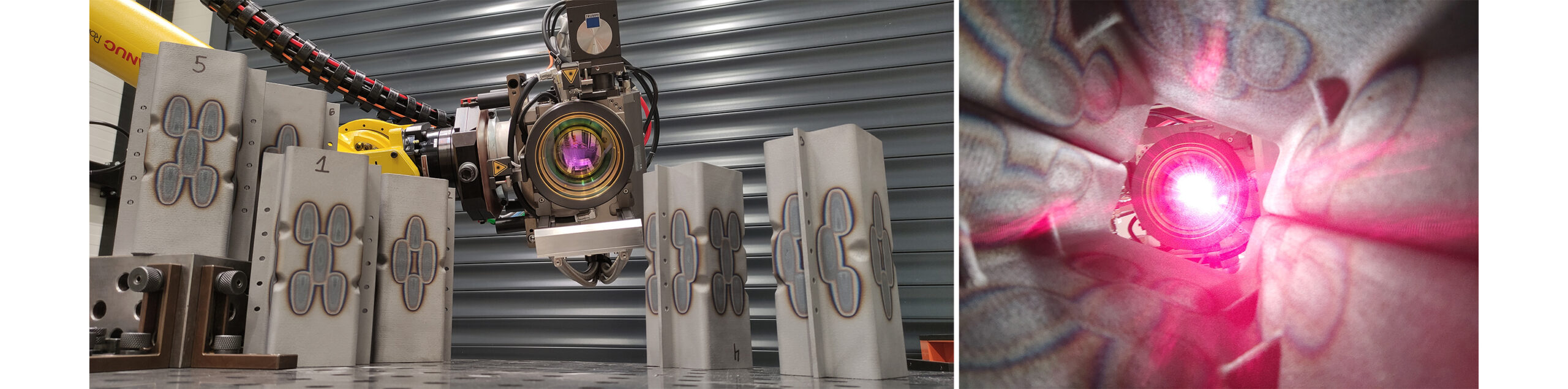

2018
Akronim: InverTec
Coordinato: EFB – European Research Association for Sheet Metal Working
Partners: IWU – Fraunhofer Institute for Machine Tools and Forming Technology, SLK – Technische Universität Chemnitz / Department of Lightweight Structures and Polymer Technology, PWr – Wroclaw University of Science and Technology, CINNOMATECH – Cluster of Innovative Manufacturing Technologies.
Lata realizacji: 2018 – 2020
Finansowanie: NCBR – Cornet-22 (CORNET/22/3/2018)
Objective:The innovative contribution of the intended research project is the development of new high performer’s inverse hybrid composite, consisting of a continuous fibre reinforced thermoplastic matrix, in which a metal insert will be integrated. Besides the improvement of crash performance, the metallic insert is to be additionally used for the effective connection of the composite to the adjacent metallic structures.
For the efficient manufacturing of the novel composite in high-volume applications, conventional sheet metal forming methods shall be used. Due to the application of established technologies, high investment costs at the SMEs were avoided and the entry barrier for the use of composite materials was lowered. The project approach has a great economic and industrial importance for SMEs in terms of weight and load equitable production of highly complex components and structures. Multi-material solutions can offer significant weight advantages in mobile applications, compared to classical metallic constructions. In consequence this is leading to significant energy savings and the reduction of CO2-emissions. The project aims to consider the following main topics:
- Load optimized inverse composite design
- Efficient manufacturing methods
- Simplified modular crash testing bench
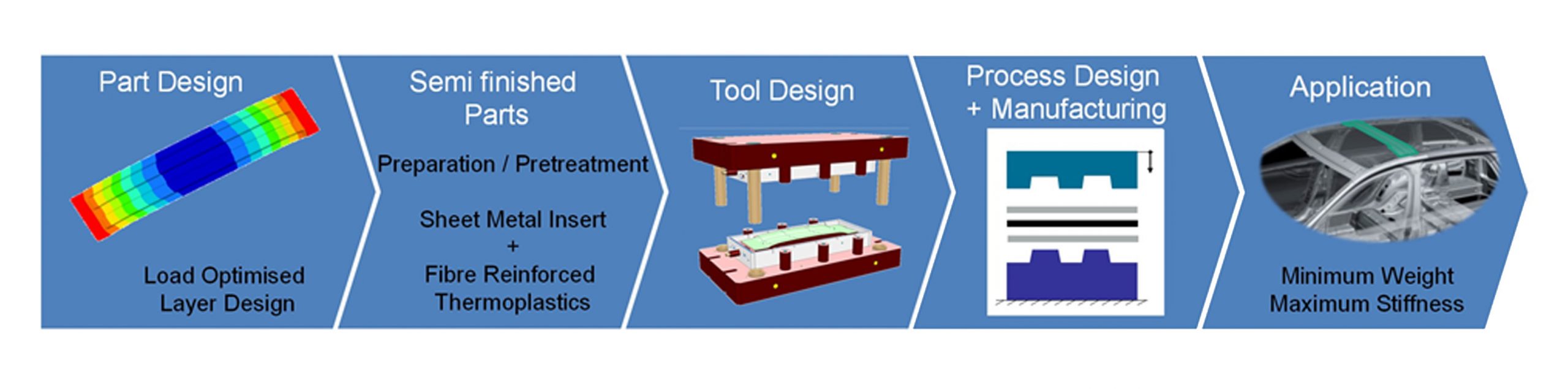
source – https://cornet.efb.de/general-description-invertec.html
